How to Protect Servers from Ransomware sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Ransomware, a digital plague that has infected countless organizations worldwide, presents a formidable threat to businesses and individuals alike.
The potential consequences of a successful ransomware attack can be devastating, ranging from data loss and system downtime to crippling financial penalties and reputational damage. This guide delves into the intricate world of ransomware, exploring its various forms, motivations, and the strategies that can be employed to safeguard your servers from this insidious threat.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to fortify your server infrastructure against ransomware attacks. We will examine the diverse tactics employed by ransomware perpetrators, explore the best practices for securing your servers, and delve into the critical importance of data backup and recovery.
By understanding the vulnerabilities and implementing the appropriate safeguards, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to this pervasive cyber threat.
Understanding Ransomware: How To Protect Servers From Ransomware
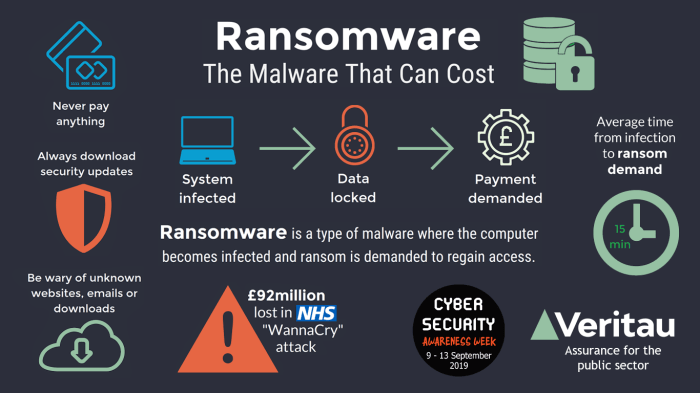
Ransomware is a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system or data until a ransom is paid. It’s a serious threat to individuals, businesses, and organizations worldwide, causing significant financial losses and disruption. Understanding the different types of ransomware attacks, their motivations, and real-world examples is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation strategies.
Types of Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks can be broadly categorized into several types, each with unique characteristics and methods of operation.
- Crypto-Ransomware:This type of ransomware encrypts files on the victim’s device, making them inaccessible. The attackers demand payment to decrypt the files and restore access.
- Locker Ransomware:Locker ransomware blocks access to the entire computer system, preventing users from logging in or accessing any files. It typically displays a message demanding payment to unlock the device.
- Scareware:Scareware, while not strictly ransomware, uses similar tactics. It tricks users into believing their computer is infected with a virus and demands payment for a fake “fix.”
- DoS (Denial of Service) Attacks:This type of attack floods the victim’s server with traffic, making it inaccessible to legitimate users. While not directly ransomware, it can be used to extort money by threatening to keep the server offline.
Motivations Behind Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks are primarily motivated by financial gain. Attackers aim to extort money from victims by holding their data hostage.
- Financial Profit:Ransomware attacks are a lucrative business for cybercriminals, as they can demand significant sums of money from victims.
- Extortion:Attackers use the threat of data loss or system downtime to force victims into paying the ransom.
- Reputation Damage:In some cases, ransomware attacks may be motivated by a desire to damage the reputation of a victim or disrupt their operations.
Real-World Examples of Ransomware Attacks
Numerous high-profile ransomware attacks have occurred in recent years, highlighting the devastating impact of this threat.
- WannaCry:This infamous ransomware attack, which began in 2017, affected thousands of computers worldwide, causing significant disruption to businesses and organizations. The attack exploited a vulnerability in Microsoft’s Windows operating system.
- NotPetya:This attack, which also occurred in 2017, was a destructive variant of ransomware that spread rapidly, causing billions of dollars in damages. The attack targeted businesses in Ukraine and globally.
- Colonial Pipeline:In 2021, the Colonial Pipeline, a major fuel pipeline in the United States, was shut down after a ransomware attack. The attack caused fuel shortages and widespread disruption.
Best Practices for Server Security
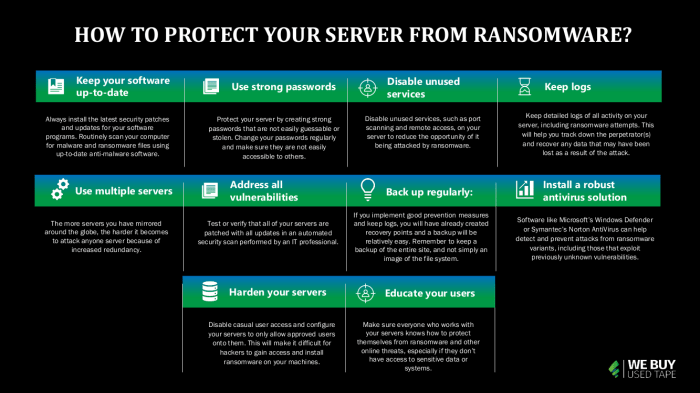
Protecting servers from ransomware attacks requires a multifaceted approach that prioritizes security best practices. Implementing a comprehensive strategy encompassing various security measures is crucial for mitigating the risk of ransomware infection and ensuring data integrity.
Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Robust passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long, include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and should not be easily guessed or found in dictionaries.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about Top Benefits of Windows 11 IoT Enterprise LTSC to enhance your awareness in the field of Top Benefits of Windows 11 IoT Enterprise LTSC.
- Password Management Tools: Utilizing password management tools can help users create and store strong passwords for multiple accounts, simplifying password management and reducing the risk of reusing passwords.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code generated by an authenticator app or sent to a registered mobile device. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access even if they obtain a password.
Regular Security Updates and Patching
Software vulnerabilities are a common entry point for ransomware attacks. Keeping software up to date with the latest security patches is essential to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
- Automatic Updates: Enabling automatic updates for operating systems and software applications ensures that systems are patched as soon as security vulnerabilities are discovered.
- Regular Patching Schedule: Establish a regular schedule for patching systems to ensure that all critical updates are applied promptly.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct regular vulnerability scans to identify and address potential weaknesses in the server’s security posture.
Network Security Measures
A robust network security strategy is crucial for protecting servers from ransomware attacks. By implementing strong network security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of malicious actors gaining access to your systems.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls act as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to your network. They examine incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking any connections that do not meet predefined security rules. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, alerting administrators to potential threats.
A firewall is a network security system that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocks any traffic that does not meet the specified security rules.
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a software application that monitors network traffic for malicious activity, such as attempts to gain unauthorized access or to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Firewall types:
- Hardware firewalls:Physical devices dedicated to filtering network traffic. They offer high performance and security but can be expensive to implement.
- Software firewalls:Software applications installed on individual devices, such as computers or servers. They are more affordable but may offer lower performance than hardware firewalls.
- Cloud firewalls:Firewalls hosted in the cloud, offering scalability and flexibility. They are ideal for organizations with a hybrid or cloud-based infrastructure.
- IDS types:
- Signature-based IDS:These systems use predefined signatures of known threats to identify malicious activity. They are effective against known threats but can be bypassed by attackers using new or unknown techniques.
- Anomaly-based IDS:These systems detect deviations from normal network behavior, identifying potential threats that may not be recognized by signature-based systems. They are more effective against unknown threats but can generate false positives.
Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments, each with its own security policies. This approach limits the impact of a successful attack, preventing attackers from accessing sensitive data or systems beyond the compromised segment.
- Benefits of network segmentation:
- Reduced attack surface:Isolating critical systems from the rest of the network limits the potential targets for attackers.
- Improved security posture:Implementing separate security policies for each segment allows for more granular control over access and traffic flow.
- Enhanced incident response:Isolating compromised segments helps to contain the spread of malware and reduces the impact of a successful attack.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms restrict user access to network resources based on predefined policies. This approach ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and systems.
- Access control methods:
- Role-based access control (RBAC):Users are assigned roles with specific permissions, granting access to resources based on their assigned roles.
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC):Access decisions are based on attributes of users, resources, and the environment, providing more granular control over access.
Securing Remote Access to Servers
Remote access to servers is often necessary for administrative tasks, but it can also pose a security risk if not properly secured.
- Best practices for securing remote access:
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA):Require strong passwords and MFA for all remote access accounts, adding an extra layer of security.
- Enable SSH port forwarding:Forward SSH traffic through a secure tunnel, encrypting all communication between the client and the server.
- Use a VPN:Connect to the server through a virtual private network (VPN), creating a secure and encrypted connection.
- Restrict remote access to authorized users:Limit remote access to only those individuals who require it for their job duties.
Data Backup and Recovery
In the face of ransomware attacks, a robust data backup and recovery strategy is the ultimate defense mechanism. It ensures business continuity by enabling the restoration of critical data, minimizing downtime, and mitigating financial losses.
Importance of Regular Data Backups
Regular data backups are crucial for safeguarding your organization’s valuable information. They serve as a safety net against various threats, including ransomware attacks, hardware failures, accidental deletions, and natural disasters. By creating periodic backups, you can restore your data to a previous state, minimizing the impact of any data loss event.
Backup Strategies and Their Advantages
Various backup strategies cater to different needs and risk profiles. Each approach offers unique advantages, allowing you to select the most suitable option for your organization.
Types of Backup Strategies
- Full Backup:This strategy creates a complete copy of all data on your server at a specific point in time. It provides the most comprehensive protection but requires significant storage space and time for backup and recovery.
- Incremental Backup:This approach backs up only the changes made since the last full or incremental backup. It reduces backup time and storage requirements but requires a full backup for initial recovery.
- Differential Backup:Similar to incremental backups, differential backups capture changes since the last full backup. However, they back up all changes made since the last full backup, regardless of whether they were backed up in previous incremental backups. This results in larger backup files than incremental backups but provides faster recovery times.
- Continuous Data Protection (CDP):This advanced strategy provides real-time data protection by continuously replicating data to a secondary location. It offers near-instant recovery and minimal data loss but requires specialized hardware and software.
Data Recovery Plan
A comprehensive data recovery plan Artikels the steps to restore your data in the event of a ransomware attack. This plan should include:
Steps for Data Recovery
- Identify and Isolate Infected Systems:Quickly identify the infected systems and isolate them from the network to prevent further spread of the ransomware.
- Restore Data from Backup:Restore data from the most recent backup that predates the ransomware attack.
- Verify Data Integrity:After restoring data, verify its integrity to ensure that the restored data is complete and accurate.
- Reinstall and Reconfigure Systems:Reinstall operating systems and applications on the affected systems and configure them to the desired settings.
- Implement Security Measures:Once systems are restored, implement security measures to prevent future attacks, including updating software, patching vulnerabilities, and implementing strong passwords.
Best Practices for Data Backup and Recovery
- Regularly Test Backup and Recovery Processes:Regularly test your backup and recovery processes to ensure they are functioning correctly. This will help identify any issues and ensure you can restore data quickly and efficiently in the event of an attack.
- Store Backups Offsite:Store backups offsite in a secure location to protect them from physical damage or theft. This can be achieved through cloud storage, a separate physical location, or a combination of both.
- Use Multiple Backup Strategies:Implement multiple backup strategies to enhance data protection. This could include a combination of full, incremental, and differential backups, as well as offsite storage.
- Regularly Update Backup Software:Ensure your backup software is up-to-date with the latest security patches and features to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Implement Data Encryption:Encrypt data backups to protect them from unauthorized access even if the backups are stolen.
Employee Training and Awareness
A well-informed workforce is the first line of defense against ransomware attacks. By educating employees about the risks, vulnerabilities, and best practices, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to these malicious threats.
Training Program for Employees
A comprehensive training program should equip employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify, avoid, and report potential ransomware threats. The training should be interactive, engaging, and tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of each employee.
- Understanding Ransomware: Explain what ransomware is, how it spreads, and the potential consequences of an infection. Provide real-life examples of ransomware attacks and their impact on businesses and individuals.
- Identifying Suspicious Emails and Attachments: Teach employees how to recognize phishing emails and malicious attachments. Emphasize the importance of verifying sender identities, scrutinizing email content, and avoiding clicking on suspicious links or opening unknown attachments.
- Social Engineering Awareness: Educate employees about social engineering techniques used by attackers to gain access to systems and data. Discuss common tactics like pretexting, baiting, and impersonation, and encourage employees to be skeptical of unsolicited requests and unusual behavior.
- Best Practices for Online Security: Reinforce good password hygiene, emphasize the importance of using strong and unique passwords for all accounts, and encourage employees to enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Reporting Suspicious Activity: Establish clear procedures for reporting suspicious emails, attachments, or any unusual activity. Ensure that employees feel comfortable reporting potential threats without fear of repercussions.
Recognizing and Reporting Suspicious Emails and Attachments
The ability to recognize and report suspicious emails and attachments is crucial for preventing ransomware attacks. Employees should be trained to identify key indicators of malicious emails and understand the appropriate steps to take when encountering them.
- Subject Line: Be wary of emails with subject lines that are vague, urgent, or contain grammatical errors.
- Sender Address: Verify the sender’s email address and ensure it aligns with the expected source. Look for typos or unusual domains.
- Content: Be cautious of emails that contain unexpected requests, threats, or promises of large rewards. Pay attention to inconsistencies or suspicious language.
- Attachments: Avoid opening attachments from unknown senders or if the content is unexpected. Hover over the attachment to view its file extension and verify it’s a known and trusted file type.
- Links: Avoid clicking on links in emails, especially if they appear suspicious or lead to unfamiliar websites. If you must click on a link, hover over it first to see the actual URL destination.
Social Engineering Awareness
Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology to manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or granting access to systems. By raising awareness about these tactics, you can empower employees to be more cautious and vigilant.
- Pretexting: Attackers use fabricated scenarios or stories to gain trust and elicit information from victims.
- Baiting: Attackers offer enticing rewards or enticements to lure victims into clicking on malicious links or downloading infected files.
- Impersonation: Attackers impersonate trusted individuals or organizations to deceive victims into providing sensitive information or granting access to systems.
Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan is crucial for organizations to effectively handle ransomware attacks. This plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of an attack, minimizing damage and ensuring a swift recovery.
Steps for Containing the Attack and Mitigating Damage
A well-defined incident response plan includes a series of steps to contain the attack and minimize damage. These steps are crucial for limiting the spread of ransomware and protecting sensitive data.
- Isolate the Infected System:Immediately disconnect the infected system from the network to prevent the ransomware from spreading to other devices. This step is critical to contain the attack and protect other systems from being compromised.
- Identify the Scope of the Attack:Determine the extent of the infection by analyzing the affected systems and identifying the type of ransomware involved. This step is important to understand the full impact of the attack and plan for recovery.
- Implement Incident Response Procedures:Follow established procedures for handling ransomware incidents, including reporting the attack to relevant authorities and activating the incident response team. These procedures ensure a coordinated and effective response to the attack.
- Collect Evidence:Gather evidence related to the attack, such as logs, system configurations, and network traffic. This evidence is crucial for forensic analysis and identifying the source of the attack.
- Restore from Backup:If possible, restore data from a clean backup to recover affected systems. This step is essential for minimizing data loss and restoring operations as quickly as possible.
Importance of Communication and Collaboration, How to Protect Servers from Ransomware
Effective communication and collaboration are vital during a ransomware incident. Open and transparent communication between the incident response team, IT staff, management, and employees ensures a coordinated response.
- Clear and Timely Communication:Keep all stakeholders informed about the situation, the steps being taken, and the expected impact. This communication helps to manage expectations and ensure everyone is working towards a common goal.
- Collaboration with External Experts:Engage external security experts, such as forensic investigators and ransomware recovery specialists, to assist in containing the attack and recovering data. These experts bring specialized knowledge and experience to the incident response process.
- Communication with Law Enforcement:Report the incident to law enforcement agencies, especially if the attack involves financial or other sensitive data. Law enforcement can investigate the attack and potentially pursue legal action against the perpetrators.
Security Tools and Technologies
The right security tools and technologies are crucial for protecting servers against ransomware attacks. These tools work in tandem to strengthen your defenses, detect suspicious activity, and mitigate the impact of an attack.
Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security solutions are essential for protecting individual computers and devices connected to your network. They provide a layered approach to security, encompassing features like:
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Protection:Endpoint security solutions include robust antivirus and anti-malware engines that can detect and remove known ransomware threats.
- Behavioral Analysis:These solutions monitor user behavior and system activity, identifying anomalies that might indicate a ransomware attack.
- File Integrity Monitoring:They track changes to critical files and folders, alerting administrators to unauthorized modifications that could be a sign of ransomware.
- Application Control:Endpoint security solutions can restrict the execution of suspicious or untrusted applications, preventing ransomware from running on your devices.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):DLP features help prevent sensitive data from being exfiltrated from your network, mitigating the potential impact of a ransomware attack.
Threat Intelligence and Vulnerability Scanning
Threat intelligence and vulnerability scanning are crucial for proactive ransomware protection.
- Threat Intelligence:Threat intelligence services provide insights into emerging ransomware threats, attack vectors, and tactics used by attackers. This information helps organizations stay ahead of the curve and tailor their defenses accordingly.
- Vulnerability Scanning:Vulnerability scanning tools identify security flaws and weaknesses in your systems and applications, including those that could be exploited by ransomware attackers. Regularly scanning your network for vulnerabilities and promptly patching them is essential.
Final Conclusion
By understanding the threat landscape, implementing robust security measures, and fostering a culture of vigilance, you can significantly mitigate the risk of a ransomware attack. This comprehensive guide has provided you with the knowledge and tools to protect your servers from this insidious threat.
Remember, vigilance, preparedness, and a proactive approach are your strongest defenses against ransomware. Stay informed, stay secure, and safeguard your digital assets.
Q&A
What are the most common types of ransomware attacks?
Ransomware attacks come in various forms, but some of the most common include:
- Crypto ransomware: This type encrypts your files, making them inaccessible until you pay a ransom.
- Locker ransomware: This type locks you out of your computer or network, preventing you from accessing your files or applications.
- DoS ransomware: This type floods your network with traffic, making your systems unresponsive and inaccessible.
How can I tell if my server has been infected with ransomware?
There are several signs that your server may have been infected with ransomware:
- Files are inaccessible or encrypted: If you cannot access your files or they have been replaced with strange file extensions, this is a strong indication of a ransomware infection.
- Ransom demands: You may receive a message demanding payment in exchange for the decryption key.
- Unusual system behavior: Your server may be running slower than usual, or you may see strange processes or programs running in the background.
- Network connectivity issues: You may experience difficulty connecting to your server or accessing network resources.
What should I do if my server is infected with ransomware?
If you suspect your server has been infected with ransomware, it is crucial to take immediate action:
- Disconnect the infected server from your network: This will prevent the ransomware from spreading to other devices.
- Contact your IT security team or a cybersecurity professional: They can help you assess the situation and determine the best course of action.
- Do not pay the ransom: Paying the ransom does not guarantee that you will get your files back, and it may encourage future attacks.
- Restore your data from backups: If you have regular backups, you can restore your data and recover from the attack.